BTC method.
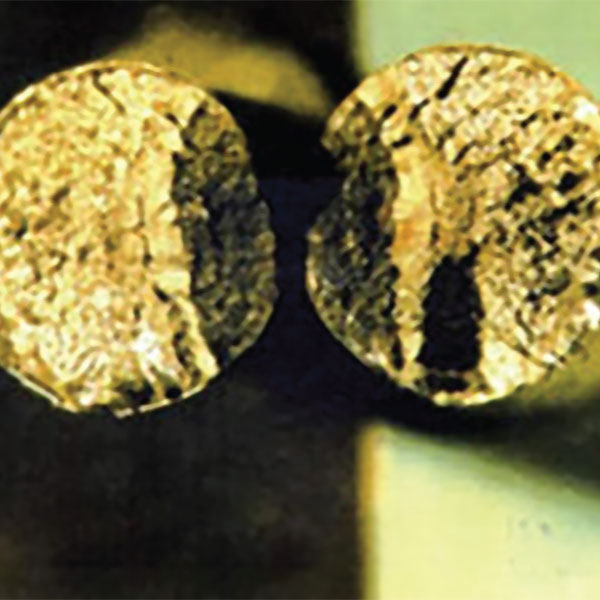
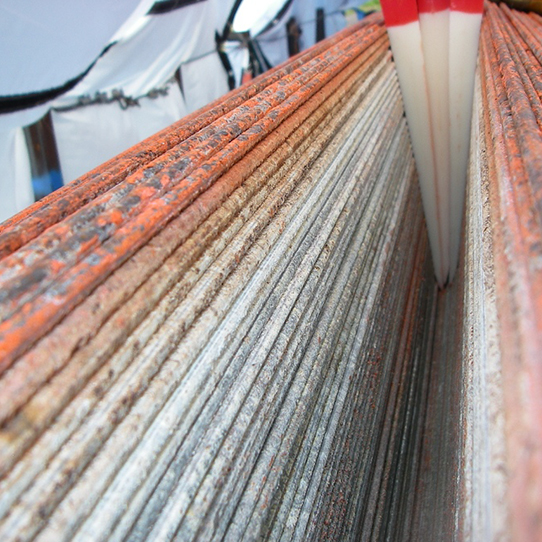
The BTC method is a comprehensive, probabilistic, state-of-the-art, and patented methodology that employs random sampling, principles of fracture mechanics, and statistical analysis for strength evaluation of bridge cables, which applies to parallel and helical; either zinc-coated or bright wire of suspension and cable-stayed bridge cables.
The BTC method provides accurate assessment of the proportions of broken and cracked wires, and forecasts service life of the bridge cable using degradation kinetics; thus providing invaluable information regarding budgeting and future inspections. These assist bridge owners in strategic planning and decision-making.
The BTC method is published in the following manuals, published and co-sponsored by the U.S. Federal Highway Administration (FHWA):
- Primer for the Inspection and Strength Evaluation of Suspension Bridge Cables, U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, Publication No. FHWA-IF-11-045, May 2012.
- BTC Method for Evaluation of Remaining Strength and Service Life of Bridge Cables-New York State Department of Transportation, NYSDOT REPORT C-07-11, September 2011.
Recent Applications of the BTC method:
The BTC method was applied for the evaluation of the remaining cable strength of the following bridges:
- Pierre Laporte Bridge, Quebec, Canada
- Forth Road Bridge, Edinburg, Scotland
- Williamsburg Bridge, New York City, USA
- Bronx-Whitestone Bridge, New York City, USA
- Mid-Hudson Bridge, Poughkeepsie, NY, USA
Peer Review
The BTC method for Cable Strength Evaluation was subject to independent peer review by different suspension bridge owners:
- MTA Bridges & Tunnels, New York City
- New York State Department of Transportation
- New York State Bridge Authority
- U.S. Federal Highway Administration (FHWA)